For some time now I have been using application based feed readers due to the lack of the ability to subscribe to authenticated feeds or to feeds that required the use of an invalid SSL certificate using a web based feed reader such as Google Reader. This has recently become really annoying as I have to use a different application based feed reader in Windows, Linux and Mac requiring me need to learn 3 different applications each of which act quite differently.
I was recently talking to a co-worker telling him that our developers would need to subscribe to our Trac RSS feed using an application based feed reader because web feed readers would not support authentication. His response was “yeah, they won’t work. the desktop ones/ff extensions suck.”
I made a decision later that day to determine a way to work around this. The solution actually came to me right away. Create a RSS proxy service where a user supplies a RSS URL, username, and password. From this information generate an alternate URL for the users use. When the user requests this alternate URL parse the URI to retrieve the original URL, username and password, then retrieve the feed on the fly and echo it back to the user.
[![FreeMyFeed][3]][3]
As my co-worker stated on his [web site][3], “It’s a crazy simple service and in hindsight I’m shocked that no one’s built such a thing before (to the best of my knowledge) - myself included.”
As I made the decision to not store any user data on my server due to security and privacy, I went with a solution that actually places the username and password in the URI. For those of you who may be concerned with this, please take comfort in knowing that the original URL, username and password are encoded in the new URI and the password is encrypted using a rotating cipher.
Without further adieu, I would like to introduce [Free My Feed][4].
[]: http://freemyfeed.com/
[3]: http://robwilkerson.org/2008/04/11/free-my-feed/
[4]: http://freemyfeed.com/
The Shadowbox JS WordPress Plugin has been updated to version 0.4. New to this update is the ability to add class=“hidden” to hide additonal links when creating an album or gallery and the ability to not include the javascript libraries in the header if you have a theme or other plugin that handles this. See the Change Log for changes. Enjoy!
If you came here looking for the plugin click here.
Update: This plugin has been tested with the new FAQ-Tastic Lite plugin and works as expected.
FAQ-Tastic is a wonderful WordPress plugin for maintaining a FAQ on your website. My company recently made a decision for one of its products to run both the blog and FAQ for the product off of WordPress. Using FAQ-Tastic will enable the folks in charge of the FAQ to make changes without having to modify any code.
While the developers of FAQ-Tastic apparently went to great lengths to add AJAX effects to the admin area for this plugin the actual display in the post or page is rather boring in the fact that it does not include any AJAX and simply displays the answer directly under the question. You can additionally list all of the questions which will link to the question and answer lower in the page but that keeps the users scrolling up and down the page. The authors of FAQ-Tastic list in their FAQ that they are planning on AJAXifying the plugin at some future time, but we don’t have time to wait for them to do it.
A simple solution would be to add a small amount of Javascript and CSS code to collapse the answers and only display them once the question has been clicked.
There is one caveat though…Ratings do not collapse with the answer, which causes them to not display correctly, and thus have been hidden using CSS in this plugin.
Now for instructions on implementing it
-
Open header.php from your WordPress theme in your favorite text editor or the WordPress theme editor.
-
Add the following code just above the line reading <?php wp_head(); ?>
-
Add the following code just after the line reading <?php wp_head(); ?>:
-
You can add some additional styling by adding a open/close indicator next to the question by adding the following into the css styles listed in step 3.
ol.faq h3 {
padding-left:20px;
background: url(/wp-content/themes/YOURTHEME/images/open.gif) top left no-repeat;
}
ol.faq h3.active {
background: url(/wp-content/themes/YOURTHEME/images/close.gif) top left no-repeat;
}
You can download these sample open/close images here
These gif images should be extracted/uploaded to ‘wp-content/themes/YOURTHEME/images’
And now that you are saying I’m not going to do this because it is too complicated…Don’t worry I have also written a plugin with the information I have provided above that will automatically implement this just by activating the plugin.
The plugin can be downloaded from WordPress.org repository.
Instructions on using the plugin
- Download the plugin from here
- Upload the ajaxify-faqtastic directory to wp-content/plugins/
- Open the admin section of WordPress, click on Plugins and then Activate this plugin.
- Simple as that…you are done.
If you don’t want to go through subscribing to a mailing list to get the FAQ-Tastic plugin, download using the following links:
Plugin
Manual
Change Log
1.4 (2009-02-27):
- Update to new version numbering
- enqueue styles and scripts instead of printing directly to the head
0.3 (2008-08-12):
- Updated for WordPress 2.6 compatibility
0.2 (2008-03-26):
Download
AJAXify FAQTastic version 1.4
Archived Versions
Update:The Lightview JS WordPress plugin is hereby completely end of life. My plugin was in conflict with the Lightview per domain license and has been removed from the WordPress plugins repository. Users seeking a Lightview WordPress plugin should see the Lightview Plus plugin written by Thorsten Puzich. As an alternative to Lightview please see my Shadowbox JS plugin.
A media viewer application written entirely in JavaScript. Using Lightview, website authors can display pictures, movies, websites, inline content and more in all major browsers without navigating away from the linking page.
This plugin uses Lightview written by Nick Stakenburg.
Javascript libraries supported are: Prototype + Scriptaculous. Prototype + Scriptaculous are included with the plugin as the versions packaged with WordPress are below the minimum requirements.
This plugin support the WordPress [ gallery] shortcode. By simply having this plugin activated and $lvGallery set to true which is the default, Lightview JS will be used to display the images in your gallery.
Screenshots
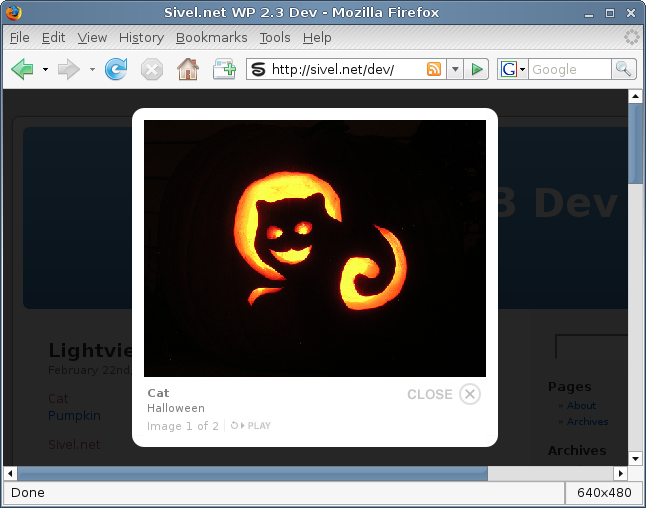
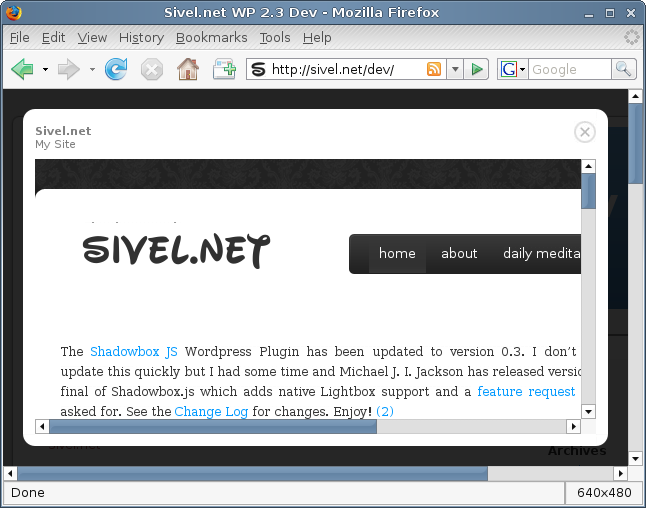
Installation
- Upload the `lightview-js` folder to the `/wp-content/plugins/` directory
- Edit lightview-js.php and modify $lvGallery based on the comments preceeding the variable. Please note that this is an optional step. Lightview JS will function properly without modification.
- Activate the plugin through the ‘Plugins’ menu in WordPress
Upgrade
- Deactivate the plugin through the ‘Plugins’ menu in WordPress
- Delete the previous `lightview-js` folder from the `/wp-content/plugins/` directory
- Upload the new `lightview-js` folder to the `/wp-content/plugins/` directory
- Edit lightview-js.php and modify $lvGallery based on the comments preceeding the variable. Please note that this is an optional step. Lightview JS will function properly without modification.
- Activate the plugin through the ‘Plugins’ menu in WordPress
Usage
-
If you are using the [ gallery] shortcode the following steps are not required. When using the [ gallery] shortcode this is automatic.
-
Create a link in your post in the following format:
<a href="http://domain.tld/directory/to/image.jpg" class="lightview">Image</a>
The above link can be to pretty much anything including websites, video files, YouTube, Google Video, inline content.
This is the minimum code required to use this plugin.
-
Please see the markup on the Lightview javascript authors usage page for more information such as sizing the media. . Please keep in mind that I did not write the Lightview javascript I only created a WordPress plugin that implements it.
-
Be sure to include `class=“lightview”` as this activates the plugin.
-
If `rel=“gallery[album]”` is included the portion listed here as `[album]` will group multiple pictures into an album called album.
NOTE: Do not use the visual editor for doing the above use the code editor. When modifying this post in the future do not use the visual editor; please use the code editor always.
Examples:
<a href="http://domain.tld/directory/to/image.jpg" class="lightview" rel="gallery[album]">Image</a>
<a href="http://domain.tld/directory/to/image.jpg" class="lightview" rel="gallery[album]"><img src="http://domain.tld/directory/to/image.jpg" /></a>
<a href="http://sivel.net/" class="lightview" rel="iframe" title="Sivel.net :: My Site :: fullscreen: true">Sivel.net</a>
Change Log
(2009-03-03):
- Plugin marked as end of life and removed due to licensing conflicts
1.5 (2009-02-27):
- enqueue styles and scripts instead of directly printing to the head
1.4 (2008-08-25):
- Updated version number scheme
- Updated code for readability
- added support for [ gallery] shortcode
0.3 (2008-08-12):
- Update for WordPress 2.6 compatibility
0.2 (2008-03-14):
Download
REMOVED
Comments
Posted February 26, 2008 by sivel
The Shadowbox JS WordPress Plugin has been updated to version 0.3. I don’t often update this quickly but I had some time and Michael J. I. Jackson has released version 1.0 final of Shadowbox.js which adds native Lightbox support and a feature request that I asked for. See the Change Log for changes. Enjoy!
Comments
Posted January 23, 2008 by sivel
I was recently had the job of displaying the most recent WordPress posts on a sites main page. The easiest way I could think of doing this is to use the RSS feed.
I’ll give two sample php functions that will do this as one requires some pear packages and the other doesn’t.
Option 1
This option requires the use of several PHP Pear packages. Those packages are XML_RSS, XML_Tree and XML_Parser. This is the preferred option as the code is specific to RSS instead of XML generically.
<?php
require_once "XML/RSS.php";
// read_rss(display_n_items,feed_url)
function read_rss($display=0,$url='') {
$rss =& new XML_RSS($url);
$rss->parse();
$itemArr = array();
foreach ($rss->getItems() as $item) {
if ($display == 0) {
break;
}
array_push($itemArr,$item);
$display--;
}
return $itemArr;
}
?>
Option 2
This option does not require any special Pear packages which would be helpful for users who do not have the capability to install them or have their hosting provider install them.
<?php
// read_rss(display_n_items,feed_url)
function read_rss($display=0,$url='') {
$doc = new DOMDocument();
$doc->load($url);
$itemArr = array();
foreach ($doc->getElementsByTagName('item') as $node) {
if ($display == 0) {
break;
}
$itemRSS = array (
'title' => $node->getElementsByTagName('title')->item(0)->nodeValue,
'description' => $node->getElementsByTagName('description')->item(0)->nodeValue,
'link' => $node->getElementsByTagName('link')->item(0)->nodeValue,
'pubdate' => $node->getElementsByTagName('pubDate')->item(0)->nodeValue
);
array_push($itemArr, $itemRSS);
$display--;
}
return $itemArr;
}
?>
Now to use either of these functions we would do something similar to the following:
<ul>
<?php
$items = read_rss(2, 'http://sivel.net/feed');
foreach ( $items as $item ) {
echo '<li><a href="' . $item['link'] . '">' . $item['title'] . '</a>';
}
?>
</ul>
Comments
Posted January 23, 2008 by sivel
Comments
Posted January 18, 2008 by sivel
I recently wrote a script that waits for something to happen and then executes a command on a remote machine via ssh. I ran into a problem where the ssh connection was established and then the ssh connection would never close.
I found out after some diagnostics that becuase there was no tty assigned to the local session that a tty was not being assigned on the remote session and for some reason ssh was not disconnecting after the command had finished.
The solution was to run the ssh command with the -t flag as such:
ssh -t -t [email protected] "somecommand"
The -t is used to force pseudo-tty allocation but when there is no local tty you must use -t -t to force tty allocation on the remote server.
Comments
Posted October 29, 2007 by sivel
Part 1 | Part 2
Back on May 23rd, 2007 I wrote an article titled Single Sign-On with Apache and Active Directory which I have now made Part 1 of this topic. In that article I wrote:
There are 3 major solutions for this which are mod_ntlm, mod_auth_kerb and Apache2:AuthenNTLM…I tried mod_ntlm which seemed to be very easy to setup and worked well. But there was one catch…If the browser did not send the NTLM information or correct NTLM information, see the footnotes1 below as to why, the user had to login with the username in the form of DOMAINusername. In my experience with applications already in place they did not require this form of DOMAINusername. This could be resolved if you could specify the default domain in mod_ntlm which you cannot.
Now I will explain why there is a Part 2 to this topic. I used the Apache2::AuthenNTLM Apache Perl module in a large environment and quickly found a serious problem which I could not diagnose or resolve. When using the Apache2::AuthenNTLM Perl module Apache would stop responding to requests to the site after an undetermined number of requests. I tried limiting the file types that would be authenticated but in the end it would still stop reaponding after a while.
So I finally decided to use the Apache mod_ntlm module to handle the authentication. And with the article I had written titled Enabling NTLM Authentication (Single Sign-On) in Firefox, the problem with having to use the username in the form of DOMAINusername in Firefox can be eliminated.
This how to is intended for CentOS 4 and RHEL4 but can be easily adapted for other distributions.
Now for the HowTo:
-
Start by installing Apache by issuing the following command:
yum install httpd
-
Next we need to install the mod_ntlm Apache module
wget http://sivel.net/repo/i386/mod_ntlm-2-0.1.el4.sn.i386.rpm
rpm -ivh mod_ntlm-2-0.1.el4.sn.i386.rpm
-
Now we need to configure mod_ntlm
cd /etc/httpd/conf.d
vi mod_ntlm.conf
Modify the conf like so (the documentation in the conf pretty much covers it also):
<location ~ "/path/to/dir/to/protect/here)/(.*)" >
# NTLMAuth - set to 'on' to activate NTLM authentication here
NTLMAuth on
# AuthNTGroups - text file containing (NT) group names and member user IDs
# NTLMBasicAuth - set to 'on' to allov Basic authentication too
# NTLMBasicRealm - realm to use for Basic authentication
# NTLMAuthoritative - set to 'off' to allow access control to be passed along to lower modules if the UserID is not known to this module
NTLMAuthoritative on
# NTLMDomain - set to the domain you want users authenticated against for cleartext authentication - if not specified, the local machine, then all trusted domains are checked
NTLMDomain MYDOMAIN
# NTLMServer - set to the NT server to contact to authenticate users
NTLMServer primary.mydomain.com
# NTLMBackup - set to the alternate NT server to contact to authenticate users
NTLMBackup secondary.mydomain.com
# NTLMLockFile - set to the lock file that is used to prevent simutaneous contacts to DC
NTLMLockfile /tmp/_mod_ntlm.lck
AuthName NTAuth
AuthType NTLM
require valid-user
Satisfy all
</location>
-
We need to modify the global conf file now.
vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Find ‘KeepAlive Off’ and change it to ‘KeepAlive On’
-
Let’s start Apache
/etc/init.d/httpd start
-
Let’s setup a simple test page that will utilize the server environment variable that mod_ntlm sets.
cd /path/set/in/step/3/in/location/directive
touch index.php
vi index.php
echo “You have logged in as ” . $_SERVER[‘REMOTE_USER’] . “”;
?>
If you do not have PHP installed you can just place a page in the directory and if you login you should be able to see it.
If you get a login prompt check the footnotes1.
Part 1 | Part 2
Footnotes
- Getting a login prompt can be caused by using Firefox with the default configuration, not being logged on in the domain that you are attempting to authenticate against, or not having the site listed in the Local Intranet security zone in Internet Explorer. Or worst of all you could have mis configured something in step 3
Comments
Posted October 26, 2007 by sivel
I have seen a good number of incoming links requesting this page that I had written back when I was using a wiki for my web site. So I decided to bring it back and make some redirects to direct people to the correct location.
With that being said these instructions are for configuring Fedora (Core 5 was used at the time) to use a Sprint PCS Connection Card to connect to the internet. I cannot verify or test this functionality as I no longer have a Sprint PCS Connection Card. So let the fun begin.
- With the Sprint PCS Connection Card PC-5740 not inserted boot up the computer into Fedora Core 5.
- Open a terminal window and SU to root.
- Execute the following command:
tail -f /var/log/messages
- Insert the card.
- You should see something similar to the following:
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: pccard: CardBus card inserted into slot 0
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: PCI: Enabling device 0000:03:00.0 (0000 -> 0002)
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: ACPI: PCI Interrupt 0000:03:00.0[A] -> Link [LNKA] -> GSI 11 (level, low) -> IRQ 11
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: ohci_hcd 0000:03:00.0: OHCI Host Controller
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: ohci_hcd 0000:03:00.0: new USB bus registered, assigned bus number 5
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: ohci_hcd 0000:03:00.0: irq 11, io mem 0xc2000000
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: usb usb5: configuration #1 chosen from 1 choice
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: hub 5-0:1.0: USB hub found
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: hub 5-0:1.0: 1 port detected
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: PCI: Enabling device 0000:03:00.1 (0000 -> 0002)
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: ACPI: PCI Interrupt 0000:03:00.1[B] -> Link [LNKA] -> GSI 11 (level, low) -> IRQ 11
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: ohci_hcd 0000:03:00.1: OHCI Host Controller
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: ohci_hcd 0000:03:00.1: new USB bus registered, assigned bus number 6
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: ohci_hcd 0000:03:00.1: irq 11, io mem 0xc2001000
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: usb usb6: configuration #1 chosen from 1 choice
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: hub 6-0:1.0: USB hub found
Aug 15 13:01:24 fedora-mobile kernel: hub 6-0:1.0: 1 port detected
Aug 15 13:01:25 fedora-mobile kernel: ohci_hcd 0000:03:00.0: wakeup
Aug 15 13:01:26 fedora-mobile kernel: usb 5-1: new full speed USB device using ohci_hcd and address 2
Aug 15 13:01:26 fedora-mobile kernel: usb 5-1: configuration #1 chosen from 1 choice
Aug 15 13:01:26 fedora-mobile kernel: cdc_acm 5-1:1.0: ttyACM0: USB ACM device
Aug 15 13:01:26 fedora-mobile kernel: usbcore: registered new driver cdc_acm
Aug 15 13:01:26 fedora-mobile kernel: drivers/usb/class/cdc-acm.c: v0.25:USB Abstract Control Model driver for USB modems and ISDN adapters
- The above is all important but the line we are most interested in is the following:
Aug 15 13:01:26 fedora-mobile kernel: cdc_acm 5-1:1.0: ttyACM0: USB ACM device
- The above line shows us that the device created is ttyACM0 which is actually located at /dev/ttyACM0.
- Assuming you are running Gnome, download and install gnome-ppp with the following:
yum install -y gnome-ppp
- In order for gnome-ppp to work properly it must be run as root.
- Open a terminal window and su to root.
- Execute gnome-ppp (Tip: You can add a " &" to the end of gnome-ppp to disconnect it from the active session allowing you to close the terminal window without closing gnome-ppp).
- Click the “Setup” button.
- Click the “Detect” button. Your modem (/dev/ttyACM0) should automatically be detected. If not then something above went wrong.
- Click the “Init Strings…” button and change “Init 2” to “ATZ” (without the quotes).
- For the username you will need to boot into Windows, open the PCS connection application and select Diagnositcs from the menu. Your username will be in the form of [email protected].
- With gnome-ppp you are required to enter a password. This will not affect the dial up seeing as though the Sprint servers wont even respond to the password being sent. So type whatever you want in this field.
- The phone number is “#777”.
- Click connect. You’re done.
- If you can’t access anything on the internet after connecting and you have IP address info, it is probably due to gnome-ppp not updating the nameserver statements in resolv.conf
Using gnome-ppp eventually got old for me so I wrote a bash script to take care of it. I won’t post extensive usage information on how to use it so use at your own risk (although I don’t see any actual risk involved).
You will need to do several things to get this up.
- Download sprint-dial.sh to your home dir or where ever you want.
wget http://cdn.sivel.net/s/p/sprint-dial.sh
- Download or configure your own .wvdial.conf and place it in your home dir and /root
wget http://cdn.sivel.net/w/v/.wvdial.conf
- Execute the script
sudo ./sprint-dial.sh
or
su
./sprint-dial.sh

